|
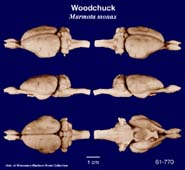
Woodchuck
(Marmota monax) #61-770 |
||||
|
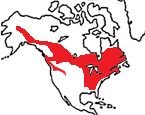
| Physical
characteristics and distribution |
|
Woodchuck
Marmota monax |
|
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home