|
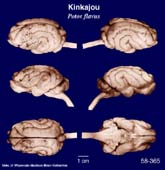
Kinkajou
(Potos flavus) #58-365 |
||||
|
| Physical
characteristics and distribution |
|
Kinkajou
P. flavus Head
and body length is 450-760 mm tail length is 392-570 mm. Weights
of adults range from 1.4-4.6 kg. with males generally being
larger than females. Coloration is tawny olive to yellowish
brown to brown on the upper parts and upper surface of the tail.
There is sometimes a black middorsal line. The undersurface
of the prehensile tail varies from yellow, buff or brownish
yellow, the muzzle is dark brown to blackish and the fur is
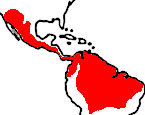
soft and woolly. P. flavus is native in Belize, Bolivia, Brazil (Mato Grosso), Columbia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Guyana, Mexico (S Tamaulipas and and Guerrero and possibly Michoacan), Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, Surinam, Venezuela. |
|
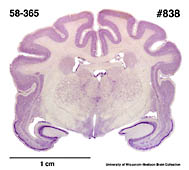
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home