|
The thalamus consists of a large collection of relatively distinct subdivisions or cellular clusters, or nuclei, all aggregated deep within the diencephalon. The thalamus contains nuclei that receive sensory input from spinal and brainstem circuits. It processes information from visual, auditory, somatic sensory, taste, pain and thermal modalities. The thalamus makes numerous interconnections with different areas of the neocortex as well as with other nuclei of the telencephalon. It receives most of its downstream inputs from a variety of neuronal clusters lying in the medulla and brainstem. The thalamus relays and translates streams of impulses arriving from all its inputs and regulates and transmits processed information to different layers of the cerebral cortex. The thalamus lies above the hypothalamus with which it makes some connections. The thalamus is symmetrically mirrored on the two sides of the brain and the two thalamic groupings abut along the midline. Some thalamic nuclei may interconnect between homologous nuclei on the two sides
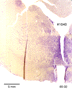
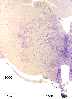
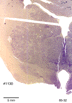
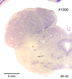
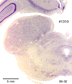
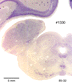
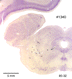
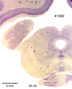
Below we display coronal sections stained for cell bodies. These cross sections are arranged from front (rostral) to back (caudal). The sequentially arranged sections are to viewed as one does in reading lines of text in a book.
The
many different named nuclear formations of the thalamus are
listed below according to terminology used by Alvin Berman and
Jerzy E. Rose.
Thalamus Parataenial
n
Anteromedial
n.
Anterodorsal
n.
Anteroventral
n.
Medioventral
n.
Nuclei of inferior thalamic peduncle
Reticular
n.
Rhomboid
n.
Ventroanterior
n.
Ventromedial
n., principal part
Ventrolateral
n.
Central
medial n.
Submedial
n.
Posterior
paraventricular n.
Paracentral
n.
Central
lateral n.
Lateral
dorsal n.
Medial
dorsal n.
Lateral
posterior n.
Ventral
basal n. ext.
Ventral
basal n. med. (arcuate)
Ventromedial
basal n.
Pulvinar
Medial
habenular n.
Lateral
habenular n.
Posterior
complex, medial
Posterior
complex, lateral
Posterior
nucleus of Rioch
Posterior
complex, intermediate
Lateral
geniculate n.
Lat
geniculate, interlaminar
Perigeniculate
n.
Parafascicular
n.
Subparafascicular
n.
Suprageniculate
n.
Medial
geniculate, magnicellular
Medial
geniculate, parvocellular
Central
medial n.
Nucleus
of brachium of inf. col.
|