|
The
Midbrain comprises the rostral portions of the brain stem. It
is in front of the medulla and lies beneath the posterior portion
of the cerebrum, and portions of its dorsal surface (superior
and inferior colliculi) lie in front of the cerebellum. The
accompanying pictures (sagittal section and ventral view) reveal
its position, and arrangement of its parts.
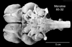

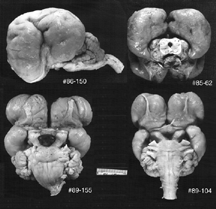 On the top of the midbrain sits the superior colliculus (a visual center) rostrally, and the inferior colliculus (an auditory center) caudally just in front of the cerebellum. On its ventral surface can be seen the two cerebral peduncles which contain the fiber tracts from the forebrain which course caudally carrying information into the midbrain, the medulla, cerebellum and spinal cord. The pons is a major protuberance lying at the caudal margin of the midbrain. The three motor nerves to the muscles of the eyes originate from motor nuclei in the midbrain. The midbrain also contains a large number of cellular groups or nuclei, as well fiber tracts and bundles. Below are displayed a number of cross sections through the Midbrain so that viewers can appreciate the complexity and diversity of architectural formations that exist within the rostral portion of the brainstem.
We present here a list of the many identified nuclear entities which lie within the midbrain portion of the brainstem. This list utilizes the nomenclature proposed in the Atlas of the brainstem by Alvin Berman.
Rostral Brainstem
Tegmentum
Caudal
Brainstem
|