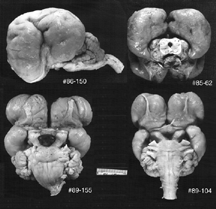
The
medulla consists of the caudal-most stalk of the brain. It is
joined with the midbrain rostrally and lies directly beneath
the cerebellum. Its caudal extent merges gradually with the
first cervical segment of the spinal cord. The accompanying
pictures (ventral view of the brain, sagittal section and several
different ventral views) reveal its position, and arrangement
of its parts.

We present below a list of the many identified nuclear entities
which lie within the medulla. This list uses the nomenclature
proposed in the Atlas of the Brainstem by Alvin Berman.
Medulla
-
Trapezoid body
- Nucleus
of trapezoid body
- Tegmental
field (gigantocellular, paralemniscal, lateral
- Preolivary
nucleus
- Superior
olive (medial, lateral)
- Trigeminal
motor nucleus
- Inferior
central nucleus
- Trigeminal
sensory nucleus(principal-dorsal-ventral, infra),
- Spinal
trigeminal (alaminar,
- Superior
vestibular (medial, lateral)
-
Lateral vestibular (medial, ventral, dorsal)
- Inferior
vestibular nucleus
- Medial
vestibular
- Cochlear
nucleus (anteroventral, posteroventral, granular layer, dorsal)
- Abducens
nucleus (6)
- Prepositus
hypoglossal nucleus
- Pospyramidal
nucl of raphe
-
Facial motor nucleus (7)
- Inferior
olivary complex (dorsal accessory, medial accessory, principal)
-
Retrofacial nucleus
- External
cuneate nucleus
- Hypoglossal
nucleus (12)
- Dorsal
motor nucleus of vagus (10)
- Lateral
reticular nucleus
- Nucleus
intercalatus
- Medial
nucleus of solitary tract
- Paramedial
reticular nucleus
- Cuneate
nuclear complex
|
