|
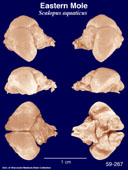
Eastern
Mole
(Scalopus aquaticus) #59-267 |
||||
|
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
The
body length of S. aquaticus is 110-170 mm, tail length
is 18-38mm. Adults weigh from 40-140 grams with males tending
to be larger than females. Color ranges from black to gray to
brown or copper. The fur is dense and velvety, covering all
but the feet, tail and tip of the snout and hiding small pairs
of eyes and ears. |
|
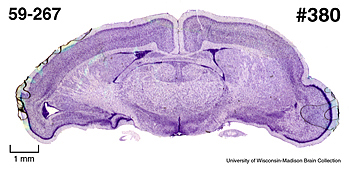
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All specimens collected followed the same preparation and histological procedure.
|
Other
Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home