|
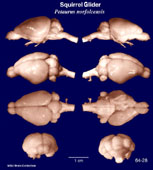
Squirrel
Glider
(Petaurus norfolcensis) #64-28 |
||||
|
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
Head and body length is 120-320 mm, tail length is 150-480 mm. The fur is fine and silky with grayish upperparts and paler underparts. A dark dorsal stripe extends from the nose to the rump and stripes on the side of the face from the nose through the eye to the ear. They have large gliding membranes which run from the outer side of the forefoot to the ankle and opens when the limbs are outstretched. The prehensile tails are furred all around. Squirrel
Gliders are similar to Sugar Gliders, in general appearance,
but are twice as large. They have more distinct facial markings,
a longer face, and a bushier tail than P. breviceps.
At times though, these two species can only be reliably distinguished
by the larger molar teeth. They are arboreal and nocturnal, preferring open forest areas. They are omnivorous, favoring sap, nectar small insects and larvae, arachnids, and small vertebrates. Females
are polyestrous and gestation is just under 3 weeks with 1
- 2 young per litter. Petaurus norfolcensis is found in Australia: E Queensland, E New South Wales, and E Victoria. |
|
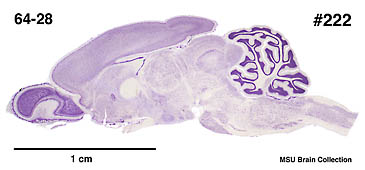
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home