|
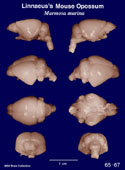
Linnaeus's
Mouse
Opossum
(Marmosa murina) #65-67 |
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
The
genus Marmosa is divided into five species groups with
a wide range of sizes and coloration. Head and body lengths
range from 85-185 mm, with tail lengths from 90-280 mm. Nearly
all forms of the genus have brown or black markings around the
eyes. The ears can be lowered by crinkling them down, similar
to the furling of a sail. Most species have short velvety fur.
M. murina has no pouch, but the tail is strongly prehensile.
The number of mammae varies from 9-19, depending on the species,
and some have pectoral as well as abdominal mammae. The
diet consists of insects and fruits, but may also contain rodents,
lizards and bird eggs. |
|
Description
of the brain
|
|
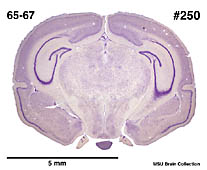
The brain weight is 767 g. The brain meaurements are: Length AP left 9.9 mm; Length AP right 9.9 mm; Bitemporal width 11.8 mm; Temporal height left 8.2 mm; Temporal height right 8.2 mm. |
|
Animal
source anf preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other
Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home