|
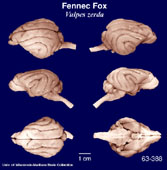
Fennec
Fox
(Vulpes zerda) #63-388 |
||||
|
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
Fennec
Fox Vulpes zerda Because
of aggressive hunting practices in the Sahara, V. zerda
is listed on Appendix 2 of the CITES. |
|
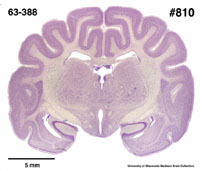
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
Our Fennec Foxspecimen was obtained from a dealer of overseas animals. It is a desert fox from Africa. All specimens collected followed the same preparation and histological procedure. |
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home