|
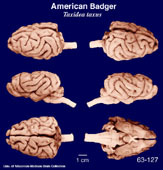
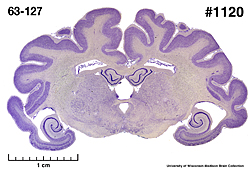
American
Badger
(Taxidea taxus) #63-127 |
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
American Badgers are a group of mostly carnivorous, medium-sized stocky mustelids. They have powerful jaws and carnassial teeth adapted for crushing, and molars that are broad, flat and multicusped. Badgers are powerfully built, wedge-shaped bodies with a small head and a short thick neck. The tail is usually short, and the snout is elongated and used for foraging. Many species dig elaborate burrow systems, making use of nonretractile claws on their forefeet. Most badgers are nocturnal, but some, including the American badger pictured here, are diurnal. Badgers have a tough skin, with long coarse guard hairs, usually with a striking facial color pattern. Most badgers eat a variety of small vertebrates, invertebrates, fruit and roots. The American Badger, is the most carnivorous, digging out chipmunks, ground squirrels, mice and rabbits. It also eats carrion and caches food. Male and female American Badgers become sexually mature as yearlings. North American badgers mate in August or September with delayed implantation until January- March. The young are born in spring in litters from 1-4. Except for sows with young, badgers are usually solitary and are aggressive to intruders to their territory. They are widespread in Canada (British Columbia. Alberta, Saskatschewan, Manitoba, Ontario), Mexico (Baja California N and C Mexico), USA (Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Michigan, Wisconsin, and most states west of the Mississippi River, except Louisiana, Arkansas). |
|
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home