|
Gray
Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus murinus) #70-145 |
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
Gray
Mouse Lemurs are among the smallest primates. Head and body
length is 125-150 mm, tail length about the same, and weight
ranges from 39-98 grams. They have soft fur, short snout,
rounded skull prominent eyes and ears, long hind limbs and
a long tail. Upper parts are usually grayish with a dark
dorsal strip and distinct white median nasal stripe. Underparts
are white. Gray Mouse Lemurs are omnivorous, eating insects, spiders, flowers, nectar, fruit, some gums, small frogs and lizards, insect secretions, and leaves. They are not true hibernators, but experience short periods of torpor during winter month. Breeding is confined to August through March with an estrous cycle of about 45-55 days. Gestation averages 60 days with average litters of 2-3 young. Young are weaned at about 25 days. Sexual maturity in females occurs at 10-29 months, males at 7-29 months. Distribution is in W Madagascar, apparently from the far southwest to the Sambirano region. |
|
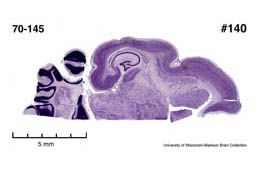
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home